Frequently Asked Questions and All "Cool Terms"
Q: What do the normal graphs look like ?
A: Below are an example of the 3D Graph, and normal graphs comparing
magnetic flux readings from multiple sensor sites.
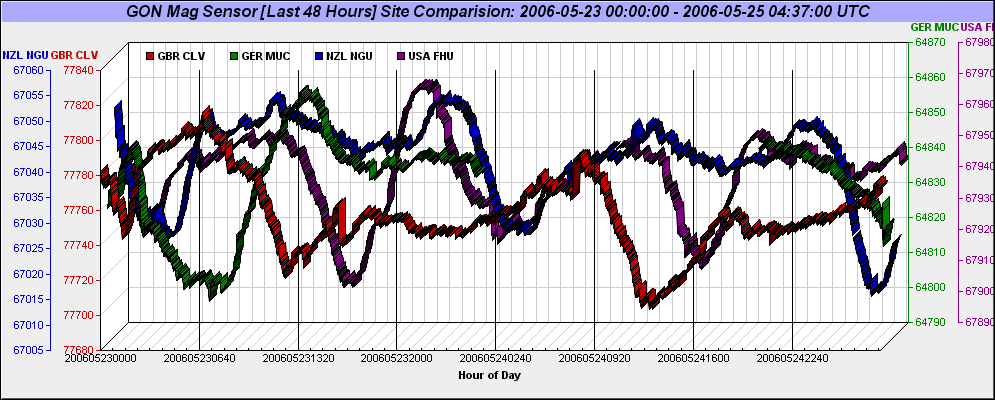
Example 3D Four Sensor Chart Depicting The Last 48 Hours Geomagnetic Flux Activity (Magnetic Flux Counts are depicted on the side of each graph associated by color):
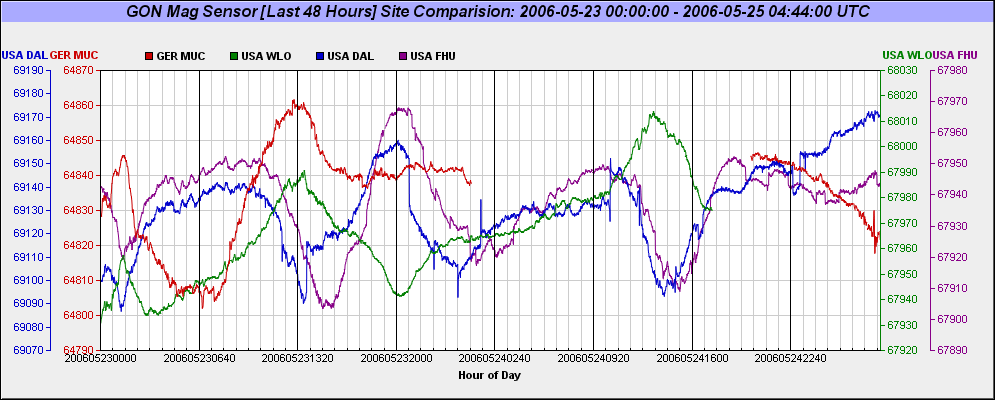
Example Four Sensor Graph Depicting The Last 48Hours Of Geomagnetic Flux Activity (Magnetic Flux Counts are depicted on the side of each graph associated by color):
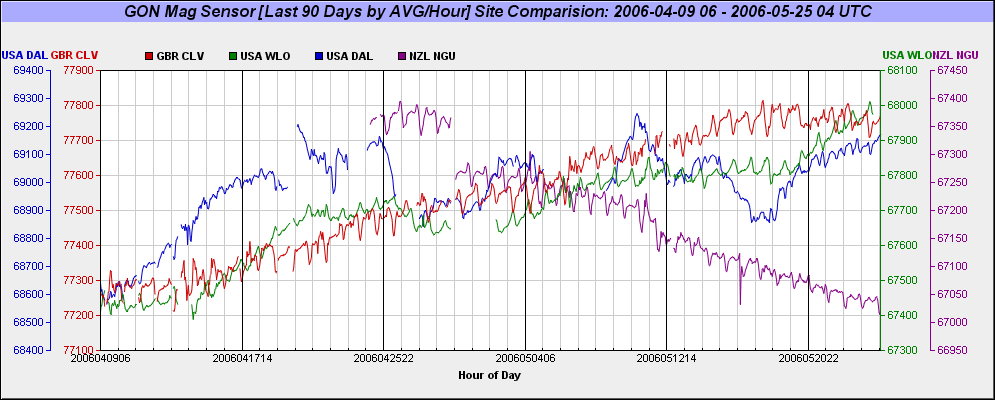
Example Four Sensor Graph Depicting The Last 90 Days Of Geomagnetic Flux Activity (Magnetic Flux Counts are depicted on the side of each graph associated by color). Notice how the southern Hemisphere Magnetic Flux (purple "NZL NGU") continues to drop as the Northern hemisphere Sensors Flux readings slowly escalate:
Real-time (RT)
- the ability of a network or system
to function and control processes within 10 minutes of occurring
Astronomical Unit (AU) - The distance from the Earth to the Sun (averaged); 1 AU is 149,597,870 kilometers (92,960,116 miles).
Solar Wind - A massive expulsion of gas and energy consisting of charged particles, mostly protons and electrons [plasma] steaming from the Sun. (Average solar wind velocities are approximately 390 kilometers per second).
Solar Prominence - An eruption of hot gases just above the photosphere of the Sun.
Solar Corona -The Sun's extremely hot outer atmosphere, overlying the visible layer called the photosphere.
Coronal Hole - a spot in the Sun's corona where the solar magnetic field lines protrude into space (vice magnetically attracted back to the sun's surface). These are often the source of lesser magnetic storms on earth and the expulsion of higher velocity solar particles (solar wind).
Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) - A fluctuation within the Sun's magnetic field in the corona resulting in the "ejection" of coronal plasma. CME's are usually the source of major magnetic storms detected on earth.
Solar Flare - This is the eruption of solar particles (energy). Solar flares are sources of massive magnetic energy and are viewed as the results of internal solar adjustments within the sun's massive fusion reactor.
Heliosphere -The heliosphere is the area in space where the sun's magnetic field extends and affects other fields originating from other sources.
Interplanetary Magnetic Field (IMF) - Solar wind (particle emissions from the sun) carries the Sun's coronal magnetic field particle emissions (interplanetary magnetic field).
Magnetosphere - The space surrounding the earth where the earth's self-generated, magnetic field is strong. This field is influenced by, the interplanetary magnetic field that originates from the Sun. The magnetosphere is loosely attached to the earth's ionosphere by currents that flow along geomagnetic field effect and can greatly influence the force of electrical currents into and out of the earth's ionosphere.